 The environment is very simple: single domain in single forest and we do not use Exchange and other stuff. Only AD and file shares.
The environment is very simple: single domain in single forest and we do not use Exchange and other stuff. Only AD and file shares.
The Windows 2008 Domain Controller is configured to be the only Adc for the domain test.local: this server is also the DNS server for this domain.
We’re going to migrate to Windows 2012 Server, and power off the Windows 2008 ADC.
First of all, I’ve installed the Windows 2012 Server and give it a static IP address, a subnet mask and set the preferred DNS server “pointing” to the existing Windows 2008 ADC only. Next we have totally updated both Servers with all the latest Windows, and verified that the date/time is correct.
Active Directory health check
A new Domain Controller installation should always start with the check of the Domain and Domain Controllers for errors that must be resolved before any other action.
Determining FSMO Role Holders
To prevent conflicting updates, the Active Directory performs updates to certain objects in a “single-master” fashion: in this mode only one DC in the entire directory is allowed to process this kind of updates.
Generaly speaking there are five FSMO roles (=Flexible Single Master Operations) that are assigned to one or more domain controllers. Every roles can update only certain objects and aspects in AD infrastructure.
Att.: In this post we are analyzing the case with only 1 DC, and for that all the roles must be associated to this unique server. But before modify something in the AD infrastructure the advice is to perform an Active Directory health check: verify who is the server that own all the FSMO roles is the first step.
Schema Master FSMO Role
The schema master FSMO role holder is the DC responsible for performing updates to the directory schema.
Domain Naming Master FSMO Role
The domain naming master FSMO role holder is the DC responsible for making changes to the forest-wide domain name space of the directory.
RID Master FSMO Role
The RID master FSMO role holder is the single DC responsible for processing RID Pool requests from all DCs within a given domain.
Att.: When a DC creates a object such as a user or group, it attaches a unique Security ID (SID) to the created object: this SID consists of a domain SID (the same for all SIDs created in a domain), and a relative ID (RID) that is unique in the domain.
PDC Emulator FSMO Role
The PDC emulator is necessary to synchronize time in an enterprise AD network.
Infrastructure FSMO Role
When an object in one domain is referenced by another object in another domain, it represents the reference by the GUID, the SID (for references to security principals), and the DN of the object being referenced. The infrastructure FSMO role holder is the DC responsible for updating an object’s SID and distinguished name in a cross-domain object reference.
How to find out which DC is holding which FSMO role? We can accomplish this task by many means, but for me the easiest way is the use of Ntdsutil command.
1) On the domain controller, click Start, click Run, type Ntdsutil in the Open box, and then click OK.
2) Type roles, and then press ENTER.
3) Type connections, and then press ENTER.
4) Type connect to server <servername>, where
5) At the server connections prompt, type q, and then press ENTER again.
6) At the FSMO maintenance prompt, type Select operation target, and then press ENTER again.
7) At the select operation target prompt, type List roles for connected server, and then press ENTER again.
C:\Windows\system32\Ntdsutil.exe: roles fsmo maintenance: connections server connections: connect to server adc-win2008 Binding a adc-win2008 in corso... Connesso a adc-win2008 tramite le credenziali dell'utente connesso localmente. server connections: q fsmo maintenance: select operation target select operation target: list roles for connected server Server "adc-win2008" riconosce i ruoli 5 Schema - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=adc-win2008,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=test,DC=local Master per la denominazione - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=adc-win2008,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=test,DC=local PDC - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=adc-win2008,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=test,DC=local RID - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=adc-win2008,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=test,DC=local Infrastrutture - CN=NTDS Settings,CN=adc-win2008,CN=Servers,CN=Default-First-Site-Name,CN=Sites,CN=Configuration,DC=test,DC=local select operation target:
If all works fine, and all the roles are associated to the windows 2008 server (adc-win2008) and there are not error, we can go further, and use the final tool dcdiag to analyzes the global state of the domain.
The following command line tools and programs will help you to verify if some problems exist within your Domain and the Domain Controllers.
On the command prompt simply digit dcdiag and then press enter.
C:\>Dcdiag Directory Server Diagnosis Performing initial setup: Trying to find home server... Home Server = adc-win2008 * Identified AD Forest. Done gathering initial info. Doing initial required tests Testing server: Default-First-Site-Name\MyServer Starting test: Connectivity ......................... adc-win2008 passed test Connectivity …...........................…
Att.: Before going any further it is necessary to check the result of dcdiag, and solve all issues identified.
Set the minimum functional level
The minimum functional level must be at least Windows Server 2003 (Windows Server 2012 computers can join a Windows AD domain running at the Windows 2003 or higher domain and forest functionality level.).
Please control that the Domain functional level is set to Windows Server 2003, in AD Users and Computer right click the “Domain Name”. Also control that the Forest functional level is set to Windows Server 2003, in AD Domains and Trusts right click “Active Directory Domains and Trusts”.
Att.: The functional level of a domain or forest controls which advanced features are available in the domain or forest. Ideally, all servers in an organization could run the latest version of Windows and take advantage of all the advanced features that are available with the newest software: but organizations often have a mixture of different versions of operating systems and for compatibility only the advanced features related to the more recent windows OS version are available. AD DS does not automatically enable advanced features, even if all domain controllers within a forest are running the same version of Windows Server. Instead, an administrator raises a domain or forest to a specific functional level to safely enable advanced features when all domain controllers in the domain or forest are running an appropriate version of Windows Server.
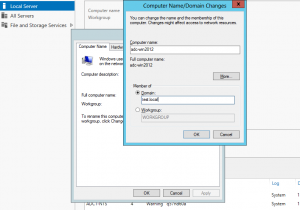
Join Windows 2012 to the domain
To join a domain, just click the current domain or workgroup name in Server Manager.
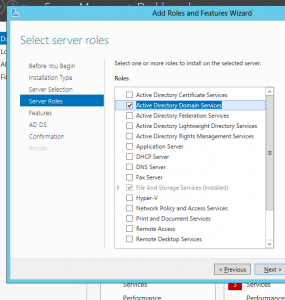
Install Active Directory Domain Services
1) Start the Server Manager and choose “Add roles and features”, in “Before you begin” click next, in the “Installation Type” use “Role-based or feature-based installation” and click Next.
2) Choose the required Server and click Next.
3) Now check the Active Directory Domain Services and in the upcoming window click the “Add features” button.
4) Leave selected Group policy management and then Click Next: after that choose “Restart the destination automatically if required” and press Install .
It may take some time, depending on the hardware.
Promote the server to be a domain controller
1) After installing the Active Directory Domain Services feature on your server, it is possibile promote it to be a domain controller. If you have just finished the feature installation, the AD DS Configuration Wizard begins automatically: however, if the feature installation has already been closed, you can start the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Window by clicking the Tasks icon along the top of Server Manager and click “Promote this server to a domain controller”.
2) Check “Add a domain controller to an existing domain”
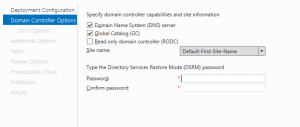
3) Choose Domain Name System (DNS) server and Global Catalog (GC) and type the Directory Services Restore Mode password and then click Next.
4) Now you wil be prompted with the warning
A delegation for this DNS server cannot be created because the authoritative parent zone cannot be found or it does not run Windows DNS server. If you are integrating with an existing DNS infrastructure, you should manually create a delegation to this DNS server in the parent zone to ensure reliable name resolution from outside the domain “test.local”. Otherwise, no action is required.
You do not need to be concerned about this warning message: click Next.
Att.: In this step the DNS delegation warning can be ignored, as the Domain Controller is for the already existing domain.
5) Choose Next and either use the default. Leave IFM (Install from media) Unchecked and click Next.
6) Location of the AD DS database, Log Files and Sysvol: here you can leave the default and click Next.
Att.: Do not store the Active Directory database, log files, or SYSVOL on a data volume formatted with Resilient File System (ReFS), the new file system avalible in Windows Server 2012. In other words Database, Log file and SYSVOL folder paths must be stored on NTFS data volumes.
7) Click Next and then Next: here information about forest, schema and domain update is shown. Click Next and a prerequisite checks will be done.
8) Review the Check (usually all the warning can be ignored) and click Install.
A reboot is required and it happens automatically by default: at the end the Windows 2012 will be a DC. Pls check the event viewer for any possible problems.
Demote the Windows 2008 server
After resolving any problems occurred in event viewer we can demote windows 2008 server.
From the command line write dcpromo and enter: accept all the default values and be careful that we do not check the value “This server is the last domain controller in the domain”.
Final checks
In the windows 2012 server pls verify that in DNS server in Windows 2012 do not remain any reference to the old Windows 2008 server.
DNS zone test.local → Properties → Name Server
You have to do the same check in the network connection: WINS, DNS, etc.
Least but not least the time server: in fact it is required to reconfigure the time service on the old and new PDCEmulator, so a recommended external time source is used.
The following command will force the time service in the new Windows 2012 server to do a syncronization, which will be reported in the System Event Log (pls check if all works fine) and set itself like a reliable time source in the AD test.local. In the command line in the windows 2012 server the the following.
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:pool.ntp.org /reliable:yes w32tm /config /update net stop w32time net start w32time
In the old Windows 2008 server run the next in an elevated command prompt: here we set the Windows 2008 like a non reliable time source.
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:domhier /reliable:no /update net stop w32time net start w32time

 Follow
Follow